Descriptive Geometry 3D DWG Plan for AutoCAD

EXERCISES AND DEMONSTRATIONS OF DESCRIPTIVE GEOMETRY APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT OF INTERSECTION VOLUMES OF PLANS, POINT, LINE, SURFACE IN SPACE 2D and 3D
Drawing labels, details, and other text information extracted from the CAD file (Translated from Spanish):
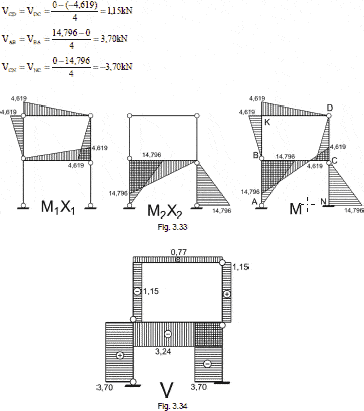
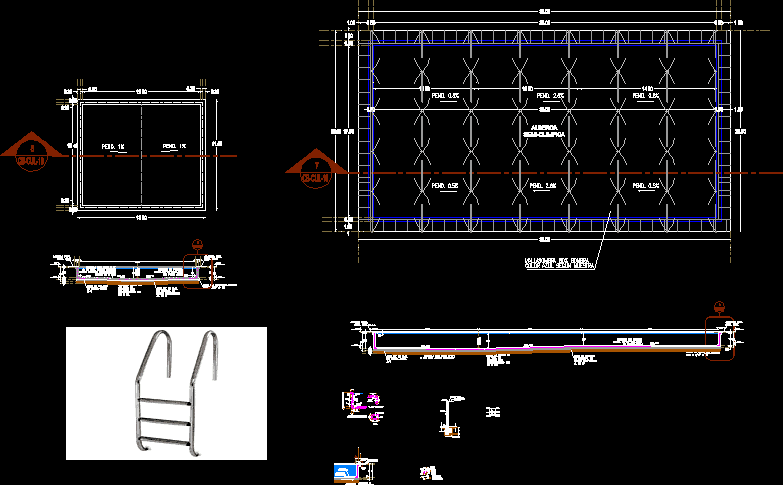
chapter viii.-, shadows, shadow projection system, shadow projected on a horizontal plane, shadow projected on a vertical plane, shadow projected on an inclined plane, spv: shadow on the vertical plane, spv: shadow on the horizontal plane, sph, sph, shadow thrown by the point, projection line, horizontal plane, vertical plane, auxiliary inclined plane, sax, pv: shadow in the horizontal plane, spv, by a vertical line, by a horizontal line, by an inclined line, chapter x.-, perspectives, point of view, plant, pv point of view, land line, distance, elevation, point, frontal, lateral elevation, chapter vii.-, warped surfaces, surface generated by a straight that slides, constantly supported in three non-coplanar straight lines. surface created by rotating a hyperbola around one of its symmetry axes. the rotation around the conjugate axis produces a hyperboloid of a leaf. the rotation around the transverse axis creates a hyperboloid of two leaves, the cylindroid is a warped surface, whose straight generatrix moves in such a way that it is continuously in contact with two direct curved lines and is always parallel to a directing plane. the curved lines guidelines can be of simple or double curvature, although in practice they are usually circles or ellipses, placed in non-parallel planes, isometry of conoid, is a curved ruled surface, generated by a straight line that moves leaning on a directrix rectilínea and a curvilinear directrix and remains parallel to a director plane. The two linear guidelines should not be located in the same plane. The curved directrix can be an open or closed curve. if the leader line is perpendicular to the direct plane the surface will be a straight conoid, otherwise it will be an oblique conoid. The conoide is a non-developable surface, a surface that is generated by the movement of a straight line, which has as guidelines a helix and its axis, and is kept parallel to a directing plane. it is considered a particular case of conoid, and as it has two mantles although in their mechanical and architectural applications, only one of them is used., chapter ix.-, transition pieces, section connections, transition pieces, stitching, length true of, the elements, mlkjn, abcdefg, cd, ba, chapter v.-, projection and development of volumes, fold lines, base, top, bottom, line, development, projection and development of volumes, prisms, note: numbers are used instead of letters to designate the projections of the prism in order to facilitate the notation used in the development., axial view of the prism, line of development, projection and development of volumes, cylinders, circumference, full development, axial view of the cylinder, pyramids, cones, lower base seen in real form in the view, real form of the upper base, complete development of the surface, vc of the plane of the lower base, complete development of the surface, parallel, elements lv, lateral edges in lv, real form of the upper base, true lengths of all the elements determined by rotation, chapter iv, relationship between straight lines, and planes in three dimensions, parallel, given plane , plane formed by a line that rotates in one of its points, a line that moves parallel to itself generates a flat surface, flat surfaces in a three-dimensional space, chapter iii, flat surfaces in a three-dimensional space, definition and generation of a flat, flat surface formed by two lines that intersect, a plane formed by two parallel lines, a plane formed by two straight lines, ab and cd, that intersect. as the line xy moves along ab and cd, it remains in contact with both lines, a plane formed by two parallel lines eg and fh. as the line xy moves along eg and fh, it remains in contact with both lines, a plane formed by a line and one outside the line, a plane formed by three noncollinear points x, y, z. the straight line the line lm passes through the point z is always in contact with the line that joins the points x, y., plane formed by a point x and the line ab. the line lm passes through point x, and when it rotates with center in x, it is always in contact with line ab., figure volumetric, line xy belongs to plane abc and passes through point p, which is also contained in the plane abc., descriptive figure, straight line of the plane, point of line and plane, horizontal line, horizontal line true magnitude, rotation method, edge view of plane abc, auxiliary horizontal line seen as a point., real form, horizontal line in plane abc, real form or true magnitude, edge view of plane abc., horizontal line, horizontal line or true magnitude, elevation view, equal and alternate angles, must be seen together in the same elevation view so that the inclinac appears
Raw text data extracted from CAD file:
| Language | Spanish |
| Drawing Type | Plan |
| Category | Handbooks & Manuals |
| Additional Screenshots |
 |
| File Type | dwg |
| Materials | Other |
| Measurement Units | Metric |
| Footprint Area | |
| Building Features | Deck / Patio |
| Tags | application, autocad, descriptive, development, DWG, exercises, geometry, intersection, line, plan, plans, point, volumes |